Solar Info
Arizona Court Again Strikes Down a HOA's Restrictions on Private Property Rights to Use Solar Energy
Read More >>
Arizona has adopted standards which require 15% of the state's energy portfolio to come exclusively from renewable sources by 2025.
SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEMS
"Solar photovoltaic systems" refers to a wide variety of solar electricity systems. Solar photovoltaic systems use solar panels made of silicon to convert sunlight into electricity.
Solar photovoltaics are used in a number of ways, primarily to power homes that are inter-tied or interconnected with the grid.
Grid interconnection - In a grid-interconnected solar power system, your photovoltaic panel or array of panels is added onto a regular source of electricity (provided by your utility company). The use of solar energy can reduce your reliance on other forms of energy to any degree you choose, depending on how big a system you purchase. Learn more about grid inter-tied solar.
SOLAR POWER USES
Solar power is used a number of different ways, of course. Solar photovoltaic energy converts the sun's radiation to usable electricity.
TWO KINDS OF SOLAR ENERGY AND FIVE WAYS THEY CAN BE USED.
Here are the three most practical and popular ways that solar energy is used:
- Integrating solar photovoltaic energy into your home or business power. In many parts of the world, solar photovoltaics is an economically feasible way to supplement the power of your home. In Japan, photovoltaics are competitive with other forms of power. In the US, new incentive programs make this form of solar energy ever more viable in many states.
- Large independent photovoltaic systems. If you have enough sun power at your site, you may be able to go off grid. You may also integrate or hybridize your solar energy system with wind power or other forms of renewable energy to stay 'off the grid.'
- Small portable solar photovoltaic systems. We see these used everywhere, from calculators to solar garden products. Portable units can be used for everything from RV appliances while single panel systems are used for traffic signs and remote monitoring stations.
TYPES OF PV SYSTEMS
PV SYSTEM COMPONENTS:
- Solar Panels - the essential component that changes light into electricity
- Inverters - the component that transforms DC into AC. an introduction to inverters
- Stand Alone Inverters - for off grid situations
- Charge Controllers - controls the energy flow and protects your battery
- Solar Batteries - "tolerant" batteries that survive frequent charging and discharging
- Battery Maintenance Grid tie Inverters (aka "Synchronous Inverters")
an inverter that allows excess electricity to flow back into the grid. - Solar panel mounts - the hardware that holds your panel in optimum basking position
- Solar panel tracking - adjusting your panels for optimum sun exposure
GLOSSARY OF ENERGY-RELATED TERMS
Check out these websites for additional information:
Where Solar Is Found
Renewable Energy Explained
POWER SYSTEM FACTS
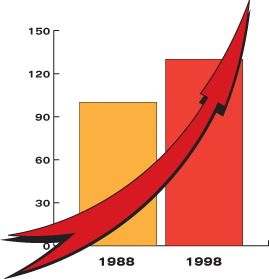
From 1988-98, U.S. electricity demand rose by nearly 30 percent. Summer peak demand is expected to increase by almost 20% during the next 10 years.
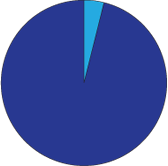
The United States accounts for
4% of the World's Population
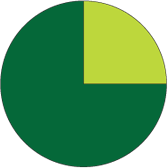
And produces 25% of its
Greenhouse Gases
Half of our country's electricity is still produced by burning coal, a rich domestic resource but a major contributor to global warming. If we are to reduce our carbon footprint and stake a claim to global environmental leadership, clean, renewable sources of energy like solar, wind and geothermal must be integrated into the nation's grid.
The electric industry is poised to make the transformation from a centralized, producer-controlled network to one that is less centralized and more consumer-interactive. The move to a smarter grid promises to change the industry's entire business model and its relationship with all stakeholders, involving and affecting utilities, regulators, energy service providers, technology and automation vendors and all consumers of electric power.
The shorter the distance from generation to consumption, the more efficient, economical and "green" it may be. It will empower consumers to become active participants in their energy choices to a degree never before possible.
